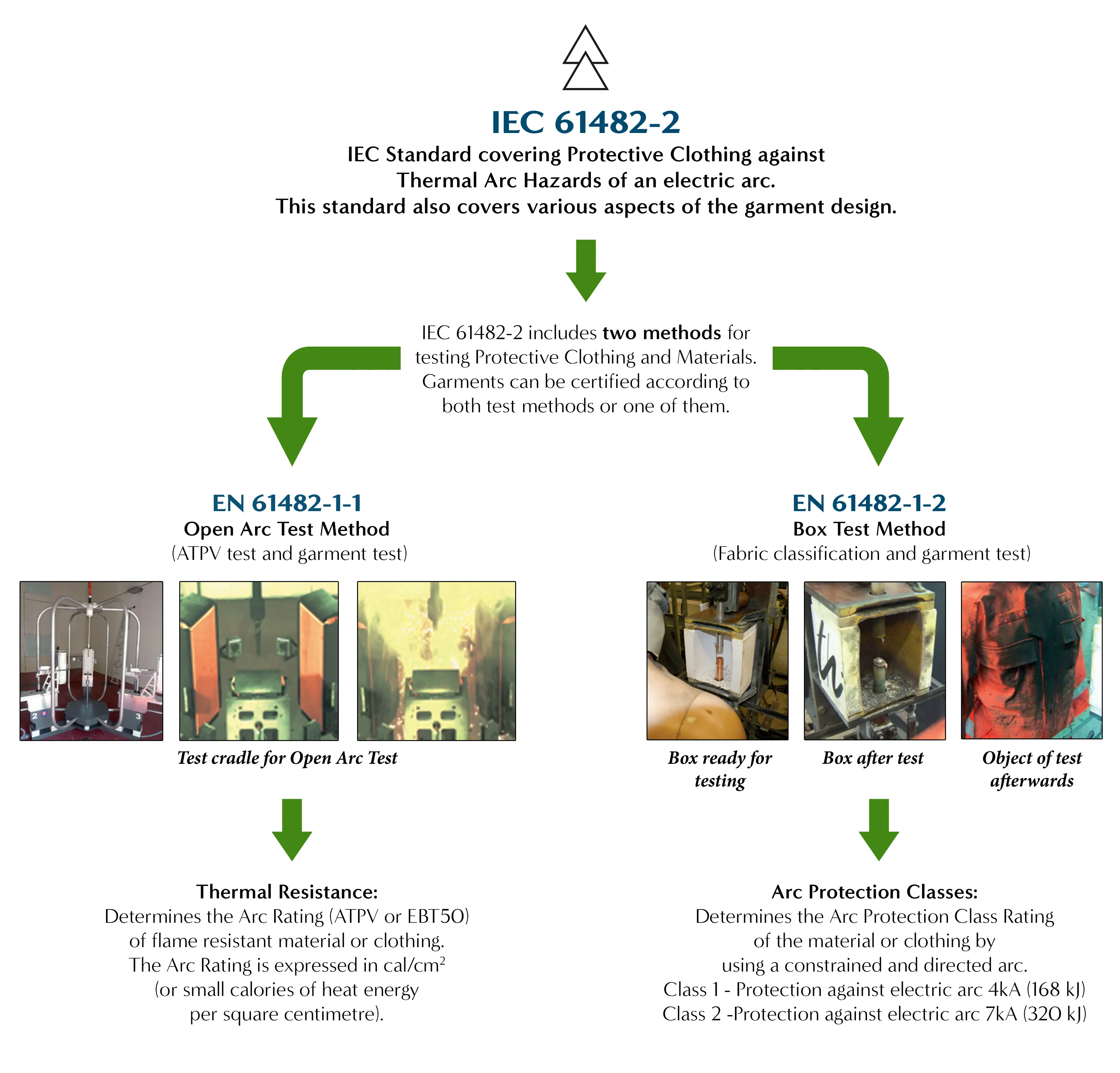
The Relationship and Differences Between IEC61482-2, IEC61482-1-1, and IEC61482-1-2
BS EN IEC61482-1-1
Work clothes - protective clothing to prevent arc heat hazards
Using open arc to measure the arc of clothing materials and protective clothing
Level (EL IM, ATPV, and/or EBT)
Pre treatment conditions: temperature between 18 ° C and 28 ° C, relative humidity between 45% and 75%, for at least 24 hours.
Washing temperature: 8.2 Pre treatment ISO 6330, method 2A, and drying through E program (drum drying) or other methods required on the label
Sample preparation: Fabric: 20 rectangular samples, Clothing: 3 sets
ISO/IEC 61482-1-1, Determine arc level through open arc testing
ELIM: The incident energy limit, usually, once the ATPV is determined, there is no need to further test the sample to determine ELIM
ATPV(Arc Thermal Protection Value) : Arc thermal performance value
EBT(Energy Breakopen Threshold): The highest thermal energy density (also measured in cal/cm ² or J/cm ²) before the material begins to fracture or crack in an open arc test
Test sample: Sample of program A (dual sensor panel test): The sample in the form of a flat material or flat material component should be cut from the clothing or constructed to represent the clothing or clothing component.
Sample size:
Length: 600mm+/-10mm
Width: 300mm+/-5mm
Sample quantity: At least 20.
The sample size after water washing pretreatment according to 8.2 should be at least 100mm higher than the actual panel length, width, and height, and should not exceed 130mm longer and wider than the panel length and width. At least 20 rectangular specimens should be prepared.
The sample should be sheared in the longitudinal or latitudinal direction of the material.
Comparison of ATPV&EBT
ATPV focuses on the maximum energy that materials can withstand without causing severe burns, therefore it pays more attention to protective performance.
EBT focuses on the ability of materials to maintain structural integrity at high energy levels, thus placing greater emphasis on the physical durability of materials.
In arc protection standards, it is usually necessary to consider both values simultaneously to comprehensively evaluate the performance of materials.